El DHA y la luteína en el bebé
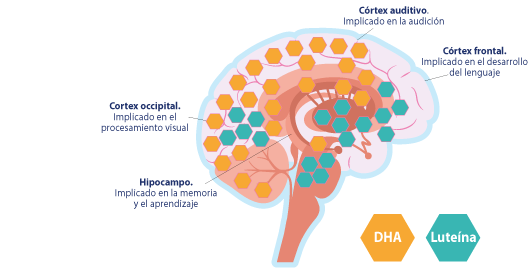
El DHA y la Luteína son componentes estructurales del cerebro y los ojos del bebé1-3.
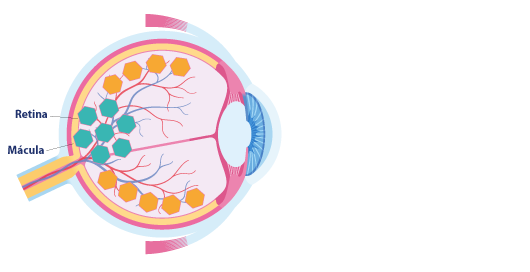
El DHA constituye hasta el 25% de los ácidos grasos del cerebro 4 y el 70% de los ácidos grasos en los fotorreceptores de la retina2.
La Luteína (junto con la zeaxantina) es el carotenoide más abundante en el cerebro5 y el único presente en la mácula del ojo6. Su concentración en la retina es 1.000 VECES más alta que en otros tejidos7. El DHA y la Luteína se encuentran en las membranas celulares y en regiones del cerebro del bebé implicadas en la memoria y el aprendizaje, la visión y audición, así como en funciones de ejecución8-10.
La Luteína es el carotenoide más abundante en la placenta y en el cordón umbilical11.
El bebé depende de los niveles de la madre (los cuales se incrementan a lo largo del embarazo)11-12.
El cuerpo humano no puede producirla, por lo que se obtendrán únicamente de la dieta11 (están presentes en algunas verduras, frutas y huevos13).
REFERENCIAS: 1.Calder PC. Docosahexaenoic Acid. Ann Nutr Metab. 2016;69 Suppl 1:7-21. 2.Calder PC. Very long-chain n-3 fatty acids and human health: fact, fiction and the future. Proc Nutr Soc. 2018 Feb;77(1):52-72. 1. 3.Krinsky NI, Landrum JT, Bone RA. Biologic mechanisms of the protective role of lutein and zeaxanthin in the eye. Annu Rev Nutr. 2003;23:171-201. 4.Valenzuela R., Morales J., Sanhueza J., Valenzuela A. Ácido docosahexaenoico (DHA), un ácido graso esencial a nivel cerebral. Rev Chil Nutr Vol. 2013; 10(4):383-390. 5.Vishwanathan R, Kuchan MJ, Sen S, Johnson EJ. Lutein and preterm infants with decreased concentrations of brain carotenoids. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2014 Nov;59(5):659-65. 6.Arunkumar R, Gorusupudi A, Bernstein PS. The macular carotenoids: A biochemical overview. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020 Nov;1865(11):158617. 7.Widomska J, Subczynski WK. Why has Nature Chosen Lutein and Zeaxanthin to Protect the Retina? J Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014 Feb 21;5(1):326. 8.Vishwanathan, R.; Schalch, W.; Johnson, E.J. Macular pigment carotenoids in the retina and occipital cortex are related in humans. Nutr. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 95–101. 9.Mohn ES, Erdman JW, Jr., Kuchan MJ, Neuringer M, Johnson EJ (2017) Lutein accumulates in subcellular membranes of brain regions in adult rhesus macaques: Relationship to DHA oxidation products. PLoS ONE 12(10):E0186767. 10.Gazzolo D, Picone S, Gaiero A, Bellettato M, Montrone G, Riccobene F, Lista G, Pellegrini G. Early Pediatric Benet of Lutein for Maturing Eyes and Brain-An Overview. Nutrients. 2021 Sep 17;13(9):3239. 11.Thoene M, Anderson-Berry A, Van Ormer M, Furtado J, Soliman GA, Goldner W, et al. Quantication of lutein + zeaxanthin presence in human placenta and correlations with blood levels and maternal dietary intake. Nutrients. 2019;11(1):134. 12.Horton, D.K., Adetona, O., Aguilar-Villalobos, M. et al. Changes in the concentrations of biochemical indicators of diet and nutritional status of pregnant women across pregnancy trimesters in Trujillo, Peru, 2004–2005. Nutr J 12, 80. 13.Eisenhauer B, Natoli S, Liew G, Flood VM. Lutein and Zeaxanthin-Food Sources, Bioavailability and Dietary Variety in Age-Related Macular Degeneration Protection. Nutrients. 2017 Feb 9;9(2):120.
